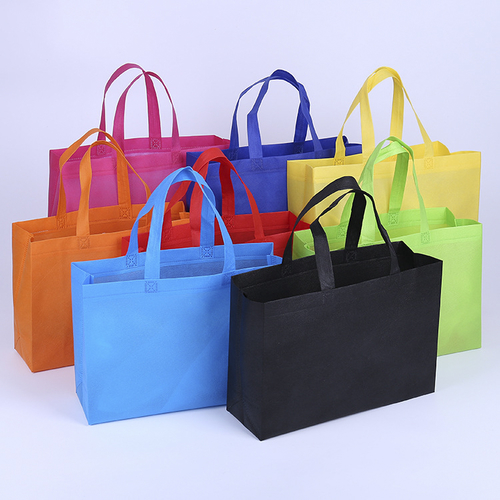
Spunbond non woven fabric is made from continuous filaments of a polymer that are bonded to each other chemically or mechanically. Its properties include good high and low temperature resistance, elongation, air permeability, UV resistance, and stability. As a result, it is a popular material for many applications.
Spunbond nonwoven fabric has numerous applications in the manufacturing industry. These versatile materials are used for many purposes, including cover backing, geotextiles, and disposable clinical/cleanliness items. The process of creating spunbond nonwoven fabric includes several steps. First, raw polypropylene fibers are spun together. Then the fibers are spun so that they overlap. This procedure creates a fabric with a unique texture.
Spunbond nonwoven fabric is a continuous filament material that can be used for a variety of applications. The process of making spunbond nonwovens involves bonding filaments directly to a web and can be done mechanically, chemically, or with air streams. As a result, spinning spunbond fabrics has a lower manufacturing cost and can increase production. Spunbond nonwovens are becoming increasingly popular in applications such as medical garments.
The production of spunbond nonwoven fabrics is complex, with many variables affecting the materials used. Polymer throughput, die temperature, and quench temperature are all important factors. Additionally, polymer types and molecular weight distribution affect the final fabric's physical and chemical performance. These factors can affect the economy of production.


 英语
英语 中文简体
中文简体